Postgresql Shared Hash Table
1. 背景
由于ptbm需要一个集中式的book keeper管理所有文件到虚拟地址的映射, 所以需要将book keeper放在共享内存中. 我们参考pg buffer manager中的hash table熟悉一下在pg中如何实现一个基于共享内存的数据结构.
2. 初始化
/*
* ShmemInitHash -- Create and initialize, or attach to, a
* shared memory hash table.
*
* We assume caller is doing some kind of synchronization
* so that two processes don't try to create/initialize the same
* table at once. (In practice, all creations are done in the postmaster
* process; child processes should always be attaching to existing tables.)
*
* max_size is the estimated maximum number of hashtable entries. This is
* not a hard limit, but the access efficiency will degrade if it is
* exceeded substantially (since it's used to compute directory size and
* the hash table buckets will get overfull).
*
* init_size is the number of hashtable entries to preallocate. For a table
* whose maximum size is certain, this should be equal to max_size; that
* ensures that no run-time out-of-shared-memory failures can occur.
*
* *infoP and hash_flags must specify at least the entry sizes and key
* comparison semantics (see hash_create()). Flag bits and values specific
* to shared-memory hash tables are added here, except that callers may
* choose to specify HASH_PARTITION and/or HASH_FIXED_SIZE.
*
* Note: before Postgres 9.0, this function returned NULL for some failure
* cases. Now, it always throws error instead, so callers need not check
* for NULL.
*/
HTAB *
ShmemInitHash(const char *name, /* table string name for shmem index */
long init_size, /* initial table size */
long max_size, /* max size of the table */
HASHCTL *infoP, /* info about key and bucket size */
int hash_flags) /* info about infoP */
{
bool found;
void *location;
/*
* Hash tables allocated in shared memory have a fixed directory; it can't
* grow or other backends wouldn't be able to find it. So, make sure we
* make it big enough to start with.
*
* The shared memory allocator must be specified too.
*/
infoP->dsize = infoP->max_dsize = hash_select_dirsize(max_size);
infoP->alloc = ShmemAllocNoError;
hash_flags |= HASH_SHARED_MEM | HASH_ALLOC | HASH_DIRSIZE;
/* look it up in the shmem index */
location = ShmemInitStruct(name,
hash_get_shared_size(infoP, hash_flags),
&found);
/*
* if it already exists, attach to it rather than allocate and initialize
* new space
*/
if (found)
hash_flags |= HASH_ATTACH;
/* Pass location of hashtable header to hash_create */
infoP->hctl = (HASHHDR *) location;
return hash_create(name, init_size, infoP, hash_flags);
}
总结一下初始化阶段的重点:
- 初始化共享内存data structure可以基于一个假设: postmaster负责初始化, backend只会attach.
- 提供max_size作为预估的内存分配, 运行时超出max_size不会报错, 但是会出现性能下降.
- info中包含了该hashtable的元信息,例如预估大小、元素分配方法等等.
2.1 下面具体分析ShmemInitHash中使用的子函数:
/*
* ShmemAllocNoError -- allocate max-aligned chunk from shared memory
*
* As ShmemAlloc, but returns NULL if out of space, rather than erroring.
*/
void *
ShmemAllocNoError(Size size)
{
Size allocated_size;
return ShmemAllocRaw(size, &allocated_size);
}
/*
* ShmemAllocRaw -- allocate align chunk and return allocated size
*
* Also sets *allocated_size to the number of bytes allocated, which will
* be equal to the number requested plus any padding we choose to add.
*/
static void *
ShmemAllocRaw(Size size, Size *allocated_size)
{
Size newStart;
Size newFree;
void *newSpace;
/*
* Ensure all space is adequately aligned. We used to only MAXALIGN this
* space but experience has proved that on modern systems that is not good
* enough. Many parts of the system are very sensitive to critical data
* structures getting split across cache line boundaries. To avoid that,
* attempt to align the beginning of the allocation to a cache line
* boundary. The calling code will still need to be careful about how it
* uses the allocated space - e.g. by padding each element in an array of
* structures out to a power-of-two size - but without this, even that
* won't be sufficient.
*/
size = CACHELINEALIGN(size);
*allocated_size = size;
Assert(ShmemSegHdr != NULL);
SpinLockAcquire(ShmemLock);
newStart = ShmemSegHdr->freeoffset;
newFree = newStart + size;
if (newFree <= ShmemSegHdr->totalsize)
{
newSpace = (void *) ((char *) ShmemBase + newStart);
ShmemSegHdr->freeoffset = newFree;
}
else
newSpace = NULL;
SpinLockRelease(ShmemLock);
/* note this assert is okay with newSpace == NULL */
Assert(newSpace == (void *) CACHELINEALIGN(newSpace));
return newSpace;
}
// ===== ShmemSegHdr的定义
static PGShmemHeader *ShmemSegHdr; /* shared mem segment header */
typedef struct PGShmemHeader /* standard header for all Postgres shmem */
{
int32 magic; /* magic # to identify Postgres segments */
#define PGShmemMagic 679834894
pid_t creatorPID; /* PID of creating process (set but unread) */
Size totalsize; /* total size of segment */
Size freeoffset; /* offset to first free space */
dsm_handle dsm_control; /* ID of dynamic shared memory control seg */
void *index; /* pointer to ShmemIndex table */
#ifndef WIN32 /* Windows doesn't have useful inode#s */
dev_t device; /* device data directory is on */
ino_t inode; /* inode number of data directory */
#endif
} PGShmemHeader;
// =======Shmem的初始化
/*
* InitShmemAccess() --- set up basic pointers to shared memory.
*
* Note: the argument should be declared "PGShmemHeader *seghdr",
* but we use void to avoid having to include ipc.h in shmem.h.
*/
void
InitShmemAccess(void *seghdr)
{
PGShmemHeader *shmhdr = (PGShmemHeader *) seghdr;
ShmemSegHdr = shmhdr;
ShmemBase = (void *) shmhdr;
ShmemEnd = (char *) ShmemBase + shmhdr->totalsize;
}
- 按照cache line对齐的大小分配
- 空间不足时会返回NULL
- 从ShmemSegHdr中获取当前free address, 顺序向后分配.
- 关于shared memory初始化, 参考:
/*
* Select an appropriate directory size for a hashtable with the given
* maximum number of entries.
* This is only needed for hashtables in shared memory, whose directories
* cannot be expanded dynamically.
* NB: assumes that all hash structure parameters have default values!
*
* XXX this had better agree with the behavior of init_htab()...
*/
long
hash_select_dirsize(long num_entries)
{
long nBuckets,
nSegments,
nDirEntries;
/* estimate number of buckets wanted */
nBuckets = next_pow2_long(num_entries);
/* # of segments needed for nBuckets */
nSegments = next_pow2_long((nBuckets - 1) / DEF_SEGSIZE + 1);
/* directory entries */
nDirEntries = DEF_DIRSIZE;
while (nDirEntries < nSegments)
nDirEntries <<= 1; /* dir_alloc doubles dsize at each call */
return nDirEntries;
}
/*
* Constants
*
* A hash table has a top-level "directory", each of whose entries points
* to a "segment" of ssize bucket headers. The maximum number of hash
* buckets is thus dsize * ssize (but dsize may be expansible). Of course,
* the number of records in the table can be larger, but we don't want a
* whole lot of records per bucket or performance goes down.
*
* In a hash table allocated in shared memory, the directory cannot be
* expanded because it must stay at a fixed address. The directory size
* should be selected using hash_select_dirsize (and you'd better have
* a good idea of the maximum number of entries!). For non-shared hash
* tables, the initial directory size can be left at the default.
*/
#define DEF_SEGSIZE 256
#define DEF_SEGSIZE_SHIFT 8 /* must be log2(DEF_SEGSIZE) */
#define DEF_DIRSIZE 256
- entry是hash table的最小单元
- 根据entry计算bucket数量
- 根据bucket计算segment数量 (每个segment中默认有256个bucket)
- 根据segment数量计算directory entries的数量 (疑惑)
/*
* Compute the required initial memory allocation for a shared-memory
* hashtable with the given parameters. We need space for the HASHHDR
* and for the (non expansible) directory.
*/
Size
hash_get_shared_size(HASHCTL *info, int flags)
{
Assert(flags & HASH_DIRSIZE);
Assert(info->dsize == info->max_dsize);
return sizeof(HASHHDR) + info->dsize * sizeof(HASHSEGMENT);
}
- 根据info中的dsize和一个HASHSEGMENT的大小计算出整个hashtable需要的空间.
/*
* hash_create -- create a new dynamic hash table
*
* tabname: a name for the table (for debugging purposes)
* nelem: maximum number of elements expected
* *info: additional table parameters, as indicated by flags
* flags: bitmask indicating which parameters to take from *info
*
* The flags value *must* include HASH_ELEM. (Formerly, this was nominally
* optional, but the default keysize and entrysize values were useless.)
* The flags value must also include exactly one of HASH_STRINGS, HASH_BLOBS,
* or HASH_FUNCTION, to define the key hashing semantics (C strings,
* binary blobs, or custom, respectively). Callers specifying a custom
* hash function will likely also want to use HASH_COMPARE, and perhaps
* also HASH_KEYCOPY, to control key comparison and copying.
* Another often-used flag is HASH_CONTEXT, to allocate the hash table
* under info->hcxt rather than under TopMemoryContext; the default
* behavior is only suitable for session-lifespan hash tables.
* Other flags bits are special-purpose and seldom used, except for those
* associated with shared-memory hash tables, for which see ShmemInitHash().
*
* Fields in *info are read only when the associated flags bit is set.
* It is not necessary to initialize other fields of *info.
* Neither tabname nor *info need persist after the hash_create() call.
*
* Note: It is deprecated for callers of hash_create() to explicitly specify
* string_hash, tag_hash, uint32_hash, or oid_hash. Just set HASH_STRINGS or
* HASH_BLOBS. Use HASH_FUNCTION only when you want something other than
* one of these.
*
* Note: for a shared-memory hashtable, nelem needs to be a pretty good
* estimate, since we can't expand the table on the fly. But an unshared
* hashtable can be expanded on-the-fly, so it's better for nelem to be
* on the small side and let the table grow if it's exceeded. An overly
* large nelem will penalize hash_seq_search speed without buying much.
*/
HTAB *
hash_create(const char *tabname, long nelem, const HASHCTL *info, int flags)
{
HTAB *hashp;
HASHHDR *hctl;
/*
* Hash tables now allocate space for key and data, but you have to say
* how much space to allocate.
*/
Assert(flags & HASH_ELEM);
Assert(info->keysize > 0);
Assert(info->entrysize >= info->keysize);
/*
* For shared hash tables, we have a local hash header (HTAB struct) that
* we allocate in TopMemoryContext; all else is in shared memory.
*
* For non-shared hash tables, everything including the hash header is in
* a memory context created specially for the hash table --- this makes
* hash_destroy very simple. The memory context is made a child of either
* a context specified by the caller, or TopMemoryContext if nothing is
* specified.
*/
if (flags & HASH_SHARED_MEM)
{
/* Set up to allocate the hash header */
CurrentDynaHashCxt = TopMemoryContext;
}
else
{
/* Create the hash table's private memory context */
if (flags & HASH_CONTEXT)
CurrentDynaHashCxt = info->hcxt;
else
CurrentDynaHashCxt = TopMemoryContext;
CurrentDynaHashCxt = AllocSetContextCreate(CurrentDynaHashCxt,
"dynahash",
ALLOCSET_DEFAULT_SIZES);
}
/* Initialize the hash header, plus a copy of the table name */
hashp = (HTAB *) DynaHashAlloc(sizeof(HTAB) + strlen(tabname) + 1);
MemSet(hashp, 0, sizeof(HTAB));
hashp->tabname = (char *) (hashp + 1);
strcpy(hashp->tabname, tabname);
/* If we have a private context, label it with hashtable's name */
if (!(flags & HASH_SHARED_MEM))
MemoryContextSetIdentifier(CurrentDynaHashCxt, hashp->tabname);
/*
* Select the appropriate hash function (see comments at head of file).
*/
if (flags & HASH_FUNCTION)
{
Assert(!(flags & (HASH_BLOBS | HASH_STRINGS)));
hashp->hash = info->hash;
}
else if (flags & HASH_BLOBS)
{
Assert(!(flags & HASH_STRINGS));
/* We can optimize hashing for common key sizes */
if (info->keysize == sizeof(uint32))
hashp->hash = uint32_hash;
else
hashp->hash = tag_hash;
}
else
{
/*
* string_hash used to be considered the default hash method, and in a
* non-assert build it effectively still is. But we now consider it
* an assertion error to not say HASH_STRINGS explicitly. To help
* catch mistaken usage of HASH_STRINGS, we also insist on a
* reasonably long string length: if the keysize is only 4 or 8 bytes,
* it's almost certainly an integer or pointer not a string.
*/
Assert(flags & HASH_STRINGS);
Assert(info->keysize > 8);
hashp->hash = string_hash;
}
/*
* If you don't specify a match function, it defaults to string_compare if
* you used string_hash, and to memcmp otherwise.
*
* Note: explicitly specifying string_hash is deprecated, because this
* might not work for callers in loadable modules on some platforms due to
* referencing a trampoline instead of the string_hash function proper.
* Specify HASH_STRINGS instead.
*/
if (flags & HASH_COMPARE)
hashp->match = info->match;
else if (hashp->hash == string_hash)
hashp->match = (HashCompareFunc) string_compare;
else
hashp->match = memcmp;
/*
* Similarly, the key-copying function defaults to strlcpy or memcpy.
*/
if (flags & HASH_KEYCOPY)
hashp->keycopy = info->keycopy;
else if (hashp->hash == string_hash)
{
/*
* The signature of keycopy is meant for memcpy(), which returns
* void*, but strlcpy() returns size_t. Since we never use the return
* value of keycopy, and size_t is pretty much always the same size as
* void *, this should be safe. The extra cast in the middle is to
* avoid warnings from -Wcast-function-type.
*/
hashp->keycopy = (HashCopyFunc) (pg_funcptr_t) strlcpy;
}
else
hashp->keycopy = memcpy;
/* And select the entry allocation function, too. */
if (flags & HASH_ALLOC)
hashp->alloc = info->alloc;
else
hashp->alloc = DynaHashAlloc;
if (flags & HASH_SHARED_MEM)
{
/*
* ctl structure and directory are preallocated for shared memory
* tables. Note that HASH_DIRSIZE and HASH_ALLOC had better be set as
* well.
*/
hashp->hctl = info->hctl;
hashp->dir = (HASHSEGMENT *) (((char *) info->hctl) + sizeof(HASHHDR));
hashp->hcxt = NULL;
hashp->isshared = true;
/* hash table already exists, we're just attaching to it */
if (flags & HASH_ATTACH)
{
/* make local copies of some heavily-used values */
hctl = hashp->hctl;
hashp->keysize = hctl->keysize;
hashp->ssize = hctl->ssize;
hashp->sshift = hctl->sshift;
return hashp;
}
}
else
{
/* setup hash table defaults */
hashp->hctl = NULL;
hashp->dir = NULL;
hashp->hcxt = CurrentDynaHashCxt;
hashp->isshared = false;
}
if (!hashp->hctl)
{
hashp->hctl = (HASHHDR *) hashp->alloc(sizeof(HASHHDR));
if (!hashp->hctl)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY),
errmsg("out of memory")));
}
hashp->frozen = false;
hdefault(hashp);
hctl = hashp->hctl;
if (flags & HASH_PARTITION)
{
/* Doesn't make sense to partition a local hash table */
Assert(flags & HASH_SHARED_MEM);
/*
* The number of partitions had better be a power of 2. Also, it must
* be less than INT_MAX (see init_htab()), so call the int version of
* next_pow2.
*/
Assert(info->num_partitions == next_pow2_int(info->num_partitions));
hctl->num_partitions = info->num_partitions;
}
if (flags & HASH_SEGMENT)
{
hctl->ssize = info->ssize;
hctl->sshift = my_log2(info->ssize);
/* ssize had better be a power of 2 */
Assert(hctl->ssize == (1L << hctl->sshift));
}
/*
* SHM hash tables have fixed directory size passed by the caller.
*/
if (flags & HASH_DIRSIZE)
{
hctl->max_dsize = info->max_dsize;
hctl->dsize = info->dsize;
}
/* remember the entry sizes, too */
hctl->keysize = info->keysize;
hctl->entrysize = info->entrysize;
/* make local copies of heavily-used constant fields */
hashp->keysize = hctl->keysize;
hashp->ssize = hctl->ssize;
hashp->sshift = hctl->sshift;
/* Build the hash directory structure */
if (!init_htab(hashp, nelem))
elog(ERROR, "failed to initialize hash table \"%s\"", hashp->tabname);
/*
* For a shared hash table, preallocate the requested number of elements.
* This reduces problems with run-time out-of-shared-memory conditions.
*
* For a non-shared hash table, preallocate the requested number of
* elements if it's less than our chosen nelem_alloc. This avoids wasting
* space if the caller correctly estimates a small table size.
*/
if ((flags & HASH_SHARED_MEM) ||
nelem < hctl->nelem_alloc)
{
int i,
freelist_partitions,
nelem_alloc,
nelem_alloc_first;
/*
* If hash table is partitioned, give each freelist an equal share of
* the initial allocation. Otherwise only freeList[0] is used.
*/
if (IS_PARTITIONED(hashp->hctl))
freelist_partitions = NUM_FREELISTS;
else
freelist_partitions = 1;
nelem_alloc = nelem / freelist_partitions;
if (nelem_alloc <= 0)
nelem_alloc = 1;
/*
* Make sure we'll allocate all the requested elements; freeList[0]
* gets the excess if the request isn't divisible by NUM_FREELISTS.
*/
if (nelem_alloc * freelist_partitions < nelem)
nelem_alloc_first =
nelem - nelem_alloc * (freelist_partitions - 1);
else
nelem_alloc_first = nelem_alloc;
for (i = 0; i < freelist_partitions; i++)
{
int temp = (i == 0) ? nelem_alloc_first : nelem_alloc;
if (!element_alloc(hashp, temp, i))
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY),
errmsg("out of memory")));
}
}
if (flags & HASH_FIXED_SIZE)
hashp->isfixed = true;
return hashp;
}
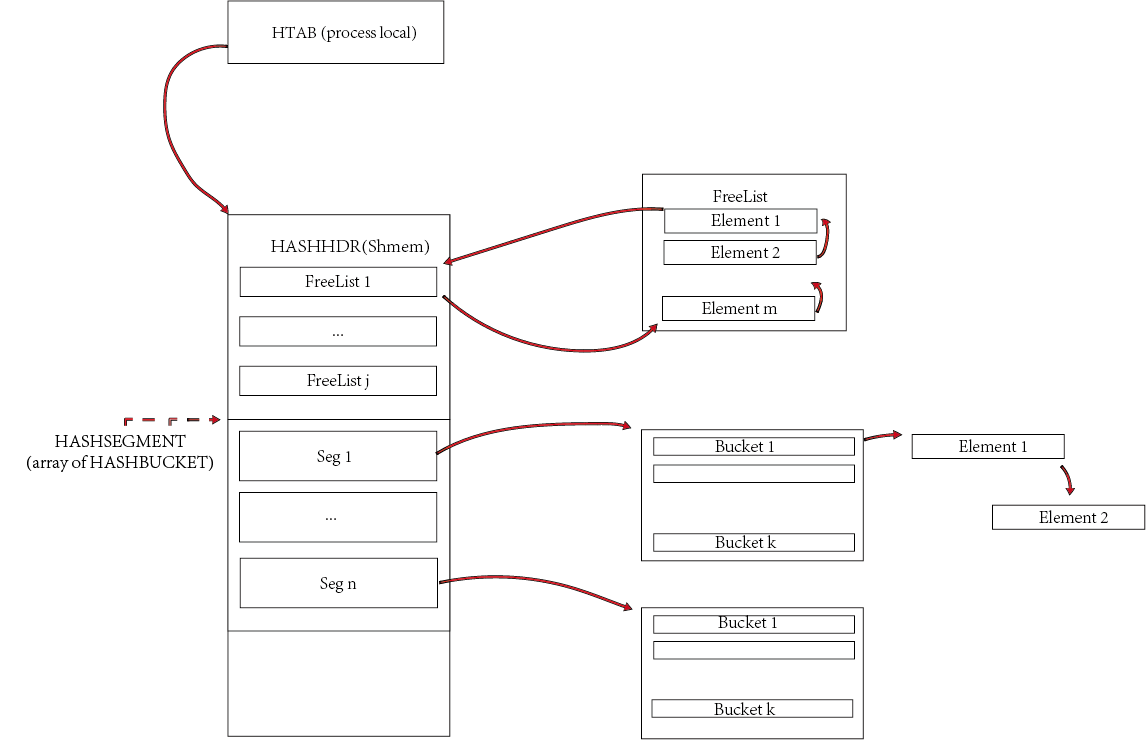
hash table有两个重要的头结构:
- HTAB (process local)
- HASHHDR (shmem)
/*
* Top control structure for a hashtable --- in a shared table, each backend
* has its own copy (OK since no fields change at runtime)
*/
struct HTAB
{
HASHHDR *hctl; /* => shared control information */
HASHSEGMENT *dir; /* directory of segment starts */
HashValueFunc hash; /* hash function */
HashCompareFunc match; /* key comparison function */
HashCopyFunc keycopy; /* key copying function */
HashAllocFunc alloc; /* memory allocator */
MemoryContext hcxt; /* memory context if default allocator used */
char *tabname; /* table name (for error messages) */
bool isshared; /* true if table is in shared memory */
bool isfixed; /* if true, don't enlarge */
/* freezing a shared table isn't allowed, so we can keep state here */
bool frozen; /* true = no more inserts allowed */
/* We keep local copies of these fixed values to reduce contention */
Size keysize; /* hash key length in bytes */
long ssize; /* segment size --- must be power of 2 */
int sshift; /* segment shift = log2(ssize) */
};
/*
* Header structure for a hash table --- contains all changeable info
*
* In a shared-memory hash table, the HASHHDR is in shared memory, while
* each backend has a local HTAB struct. For a non-shared table, there isn't
* any functional difference between HASHHDR and HTAB, but we separate them
* anyway to share code between shared and non-shared tables.
*/
struct HASHHDR
{
/*
* The freelist can become a point of contention in high-concurrency hash
* tables, so we use an array of freelists, each with its own mutex and
* nentries count, instead of just a single one. Although the freelists
* normally operate independently, we will scavenge entries from freelists
* other than a hashcode's default freelist when necessary.
*
* If the hash table is not partitioned, only freeList[0] is used and its
* spinlock is not used at all; callers' locking is assumed sufficient.
*/
FreeListData freeList[NUM_FREELISTS];
/* These fields can change, but not in a partitioned table */
/* Also, dsize can't change in a shared table, even if unpartitioned */
long dsize; /* directory size */
long nsegs; /* number of allocated segments (<= dsize) */
uint32 max_bucket; /* ID of maximum bucket in use */
uint32 high_mask; /* mask to modulo into entire table */
uint32 low_mask; /* mask to modulo into lower half of table */
/* These fields are fixed at hashtable creation */
Size keysize; /* hash key length in bytes */
Size entrysize; /* total user element size in bytes */
long num_partitions; /* # partitions (must be power of 2), or 0 */
long max_dsize; /* 'dsize' limit if directory is fixed size */
long ssize; /* segment size --- must be power of 2 */
int sshift; /* segment shift = log2(ssize) */
int nelem_alloc; /* number of entries to allocate at once */
#ifdef HASH_STATISTICS
/*
* Count statistics here. NB: stats code doesn't bother with mutex, so
* counts could be corrupted a bit in a partitioned table.
*/
long accesses;
long collisions;
#endif
};
/*
* HASHELEMENT is the private part of a hashtable entry. The caller's data
* follows the HASHELEMENT structure (on a MAXALIGN'd boundary). The hash key
* is expected to be at the start of the caller's hash entry data structure.
*/
typedef struct HASHELEMENT
{
struct HASHELEMENT *link; /* link to next entry in same bucket */
uint32 hashvalue; /* hash function result for this entry */
} HASHELEMENT;
在hash_create中, 主要做了以下几件事(着重分析共享内存中hash table的初始化):
- 分配hash header - HTAB
- 初始化 HTAB成员
- 哈希表名称
- 哈希函数
- 匹配函数
- key copy函数
- 元素alloc函数
- hctl (指向HASSHDR, 即共享内存中的首地址)
- dir (指向HASSHDR后的空闲地址.)
- 初始化 HASSHDR成员
- partition数量
- 初始化directory size (存疑)
- 初始化key size, entry size
- 调用init_htab(hashp, nelem) // nelem: maximum number of elements expected
/*
* Compute derived fields of hctl and build the initial directory/segment
* arrays
*/
static bool
init_htab(HTAB *hashp, long nelem)
{
HASHHDR *hctl = hashp->hctl;
HASHSEGMENT *segp;
int nbuckets;
int nsegs;
int i;
/*
* initialize mutexes if it's a partitioned table
*/
if (IS_PARTITIONED(hctl))
for (i = 0; i < NUM_FREELISTS; i++)
SpinLockInit(&(hctl->freeList[i].mutex));
/*
* Allocate space for the next greater power of two number of buckets,
* assuming a desired maximum load factor of 1.
*/
nbuckets = next_pow2_int(nelem);
/*
* In a partitioned table, nbuckets must be at least equal to
* num_partitions; were it less, keys with apparently different partition
* numbers would map to the same bucket, breaking partition independence.
* (Normally nbuckets will be much bigger; this is just a safety check.)
*/
while (nbuckets < hctl->num_partitions)
nbuckets <<= 1;
hctl->max_bucket = hctl->low_mask = nbuckets - 1;
hctl->high_mask = (nbuckets << 1) - 1;
/*
* Figure number of directory segments needed, round up to a power of 2
*/
nsegs = (nbuckets - 1) / hctl->ssize + 1;
nsegs = next_pow2_int(nsegs);
/*
* Make sure directory is big enough. If pre-allocated directory is too
* small, choke (caller screwed up).
*/
if (nsegs > hctl->dsize)
{
if (!(hashp->dir))
hctl->dsize = nsegs;
else
return false;
}
/* Allocate a directory */
if (!(hashp->dir))
{
CurrentDynaHashCxt = hashp->hcxt;
hashp->dir = (HASHSEGMENT *)
hashp->alloc(hctl->dsize * sizeof(HASHSEGMENT));
if (!hashp->dir)
return false;
}
/* Allocate initial segments */
for (segp = hashp->dir; hctl->nsegs < nsegs; hctl->nsegs++, segp++)
{
*segp = seg_alloc(hashp);
if (*segp == NULL)
return false;
}
/* Choose number of entries to allocate at a time */
hctl->nelem_alloc = choose_nelem_alloc(hctl->entrysize);
#ifdef HASH_DEBUG
fprintf(stderr, "init_htab:\n%s%p\n%s%ld\n%s%ld\n%s%d\n%s%ld\n%s%u\n%s%x\n%s%x\n%s%ld\n",
"TABLE POINTER ", hashp,
"DIRECTORY SIZE ", hctl->dsize,
"SEGMENT SIZE ", hctl->ssize,
"SEGMENT SHIFT ", hctl->sshift,
"MAX BUCKET ", hctl->max_bucket,
"HIGH MASK ", hctl->high_mask,
"LOW MASK ", hctl->low_mask,
"NSEGS ", hctl->nsegs);
#endif
return true;
}
- 初始化freeList[i].mutex
- 初始化nbuckets (每个bucket一个entry)
- 初始化max_bucket, low_mask, high_mask(存疑)
- 计算nsegs(segment数量)
- 分配segment
- 初始化nelem_alloc(一次性分配的元素个数)
/*
* allocate some new elements and link them into the indicated free list
*/
static bool
element_alloc(HTAB *hashp, int nelem, int freelist_idx)
{
HASHHDR *hctl = hashp->hctl;
Size elementSize;
HASHELEMENT *firstElement;
HASHELEMENT *tmpElement;
HASHELEMENT *prevElement;
int i;
if (hashp->isfixed)
return false;
/* Each element has a HASHELEMENT header plus user data. */
elementSize = MAXALIGN(sizeof(HASHELEMENT)) + MAXALIGN(hctl->entrysize);
CurrentDynaHashCxt = hashp->hcxt;
firstElement = (HASHELEMENT *) hashp->alloc(nelem * elementSize);
if (!firstElement)
return false;
/* prepare to link all the new entries into the freelist */
prevElement = NULL;
tmpElement = firstElement;
for (i = 0; i < nelem; i++)
{
tmpElement->link = prevElement;
prevElement = tmpElement;
tmpElement = (HASHELEMENT *) (((char *) tmpElement) + elementSize);
}
/* if partitioned, must lock to touch freeList */
if (IS_PARTITIONED(hctl))
SpinLockAcquire(&hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].mutex);
/* freelist could be nonempty if two backends did this concurrently */
firstElement->link = hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].freeList;
hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].freeList = prevElement;
if (IS_PARTITIONED(hctl))
SpinLockRelease(&hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].mutex);
return true;
}
2.2 初始化shmem data structure的时机
CreateSharedMemoryAndSemaphores
- InitBufferPool
- StrategyInitialize
- InitBufTable
- ShmemInitHash
Static HTAB *SharedBufHash
3. 使用shmem data structure
摘取一段hash_create中的注释:
/* For shared hash tables, we have a local hash header (HTAB struct) that
we allocate in TopMemoryContext; all else is in shared memory. */
HTAB(hash 表头)是process local的变量. 所以使用shared hash table的第一步是: 每个backend进程创建HTAB, 并且将HTAB指向共享内存.
pg在fork backend进程时, 会在每个backend进程初始化时调用InitBufTable. 而InitBufTable中又调用了ShmemInitHash(). 也就是说每个shared data structure除了需要在postmaster中使用ShmemInitxxx()初始化之外, 还需在backend进程中重新调用ShmemInitxxx()找到共享内存的位置.第一次调用时, pg会在shmem index中创建该数据结构. 第二次调用时, 查找shmem index获取其在shmem中的具体位置.
后续得到shared data structure的地址后, 使用对应的访问函数操作即可.
3.1 hash search
/*
* hash_search -- look up key in table and perform action
* hash_search_with_hash_value -- same, with key's hash value already computed
*
* action is one of:
* HASH_FIND: look up key in table
* HASH_ENTER: look up key in table, creating entry if not present
* HASH_ENTER_NULL: same, but return NULL if out of memory
* HASH_REMOVE: look up key in table, remove entry if present
*
* Return value is a pointer to the element found/entered/removed if any,
* or NULL if no match was found. (NB: in the case of the REMOVE action,
* the result is a dangling pointer that shouldn't be dereferenced!)
*
* HASH_ENTER will normally ereport a generic "out of memory" error if
* it is unable to create a new entry. The HASH_ENTER_NULL operation is
* the same except it will return NULL if out of memory.
*
* If foundPtr isn't NULL, then *foundPtr is set true if we found an
* existing entry in the table, false otherwise. This is needed in the
* HASH_ENTER case, but is redundant with the return value otherwise.
*
* For hash_search_with_hash_value, the hashvalue parameter must have been
* calculated with get_hash_value().
*/
void *
hash_search(HTAB *hashp,
const void *keyPtr,
HASHACTION action,
bool *foundPtr)
{
return hash_search_with_hash_value(hashp,
keyPtr,
hashp->hash(keyPtr, hashp->keysize),
action,
foundPtr);
}
void *
hash_search_with_hash_value(HTAB *hashp,
const void *keyPtr,
uint32 hashvalue,
HASHACTION action,
bool *foundPtr)
{
HASHHDR *hctl = hashp->hctl;
int freelist_idx = FREELIST_IDX(hctl, hashvalue);
Size keysize;
uint32 bucket;
long segment_num;
long segment_ndx;
HASHSEGMENT segp;
HASHBUCKET currBucket;
HASHBUCKET *prevBucketPtr;
HashCompareFunc match;
#ifdef HASH_STATISTICS
hash_accesses++;
hctl->accesses++;
#endif
/*
* If inserting, check if it is time to split a bucket.
*
* NOTE: failure to expand table is not a fatal error, it just means we
* have to run at higher fill factor than we wanted. However, if we're
* using the palloc allocator then it will throw error anyway on
* out-of-memory, so we must do this before modifying the table.
*/
if (action == HASH_ENTER || action == HASH_ENTER_NULL)
{
/*
* Can't split if running in partitioned mode, nor if frozen, nor if
* table is the subject of any active hash_seq_search scans.
*/
if (hctl->freeList[0].nentries > (long) hctl->max_bucket &&
!IS_PARTITIONED(hctl) && !hashp->frozen &&
!has_seq_scans(hashp))
(void) expand_table(hashp);
}
/*
* Do the initial lookup
*/
bucket = calc_bucket(hctl, hashvalue);
segment_num = bucket >> hashp->sshift;
segment_ndx = MOD(bucket, hashp->ssize);
segp = hashp->dir[segment_num];
if (segp == NULL)
hash_corrupted(hashp);
prevBucketPtr = &segp[segment_ndx];
currBucket = *prevBucketPtr;
/*
* Follow collision chain looking for matching key
*/
match = hashp->match; /* save one fetch in inner loop */
keysize = hashp->keysize; /* ditto */
while (currBucket != NULL)
{
if (currBucket->hashvalue == hashvalue &&
match(ELEMENTKEY(currBucket), keyPtr, keysize) == 0)
break;
prevBucketPtr = &(currBucket->link);
currBucket = *prevBucketPtr;
#ifdef HASH_STATISTICS
hash_collisions++;
hctl->collisions++;
#endif
}
if (foundPtr)
*foundPtr = (bool) (currBucket != NULL);
/*
* OK, now what?
*/
switch (action)
{
case HASH_FIND:
if (currBucket != NULL)
return (void *) ELEMENTKEY(currBucket);
return NULL;
case HASH_REMOVE:
if (currBucket != NULL)
{
/* if partitioned, must lock to touch nentries and freeList */
if (IS_PARTITIONED(hctl))
SpinLockAcquire(&(hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].mutex));
/* delete the record from the appropriate nentries counter. */
Assert(hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].nentries > 0);
hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].nentries--;
/* remove record from hash bucket's chain. */
*prevBucketPtr = currBucket->link;
/* add the record to the appropriate freelist. */
currBucket->link = hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].freeList;
hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].freeList = currBucket;
if (IS_PARTITIONED(hctl))
SpinLockRelease(&hctl->freeList[freelist_idx].mutex);
/*
* better hope the caller is synchronizing access to this
* element, because someone else is going to reuse it the next
* time something is added to the table
*/
return (void *) ELEMENTKEY(currBucket);
}
return NULL;
case HASH_ENTER:
case HASH_ENTER_NULL:
/* Return existing element if found, else create one */
if (currBucket != NULL)
return (void *) ELEMENTKEY(currBucket);
/* disallow inserts if frozen */
if (hashp->frozen)
elog(ERROR, "cannot insert into frozen hashtable \"%s\"",
hashp->tabname);
currBucket = get_hash_entry(hashp, freelist_idx);
if (currBucket == NULL)
{
/* out of memory */
if (action == HASH_ENTER_NULL)
return NULL;
/* report a generic message */
if (hashp->isshared)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY),
errmsg("out of shared memory")));
else
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY),
errmsg("out of memory")));
}
/* link into hashbucket chain */
*prevBucketPtr = currBucket;
currBucket->link = NULL;
/* copy key into record */
currBucket->hashvalue = hashvalue;
hashp->keycopy(ELEMENTKEY(currBucket), keyPtr, keysize);
/*
* Caller is expected to fill the data field on return. DO NOT
* insert any code that could possibly throw error here, as doing
* so would leave the table entry incomplete and hence corrupt the
* caller's data structure.
*/
return (void *) ELEMENTKEY(currBucket);
}
elog(ERROR, "unrecognized hash action code: %d", (int) action);
return NULL; /* keep compiler quiet */
}
- 遇到插入操作时, 决定是否扩容.
- 由哈希值计算应该落入哪一个bucket.
max bucket
|-------------|-----|---------|
low mask. high mask
根据max bucket计算出一个二次幂对齐的low mask. high mask是 low mask的两倍. 给定哈希值h, 计算 h bit or high_mask, 计算结果一定在0 - high_mask之间. 如果计算结果小于max_bucket, 则计算结果就是bucket的编号, 否则说明计算结果处于max_bucket - high_mask之间, 此时需要将计算结果和 low_mask做位与, 将bucket偏移到0 - low_mask之间.
- 根据bucket编号找到对应的bucket, 如果分段, 则需要在分段中寻找bucket
- find, enter, remove操作都需要首先遍历bucket, 尝试寻找对应的key
- find: 找到返回entry, 找不到返回nul
- enter: 找到返回entry, 找不到从freelist分配entry, 插入bucket链表
- remove: 找到从bucket链表删除entry, 放回对应的freelist.